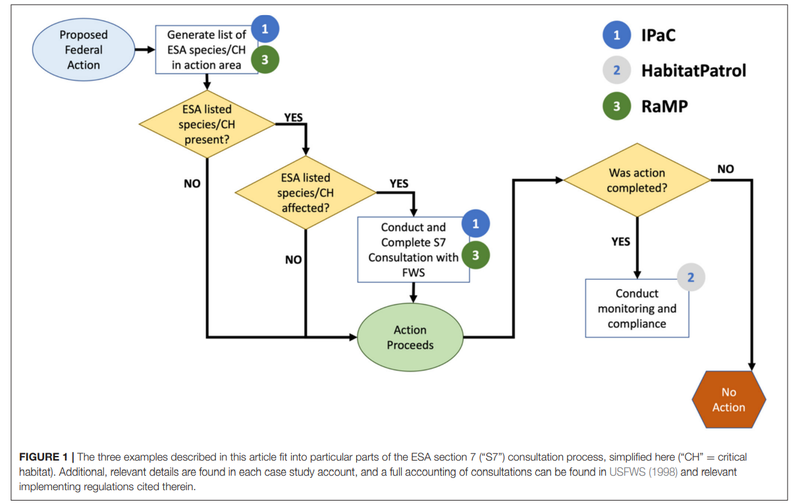

Addressing the biodiversity crisis will mean developing and adopting new resources and methods that effectively improve public conservation efforts. Technologies have a long track record of increasing the efficiency of carrying out time-consuming tasks or even making new feats possible, and if applied thoughtfully, can serve as a key means of strengthening conservation outcomes. Yet technology development sometimes proceeds without clear mechanisms for application and scaling, or key adopters like government agencies are not able to use the technologies. To overcome these discrepancies, we recommend the use of a coproduction model of conservation technology development that starts from detailed knowledge of conservation laws, regulations, and policies; identifies choke points in those processes amenable to technological solutions; and then develops those solutions while integrating existing users and needs. To illustrate the model, we describe three tools recently developed to help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of implementing the U.S. Endangered Species Act. We also highlight several outstanding questions and challenges that the broad conservation technology and policy communities may help address.